What Is cURL In PHP And How To Use?
In web development, the ability to communicate with other servers over the HTTP protocol is crucial. PHP, being a versatile language for web development, provides various methods to achieve this, and one of the most powerful tools in its arsenal is cURL (Client URL Library).
In this tutorial you will learn what is this cURL and how to use this Library in PHP to communicate with other servers.
What is cURL?
cURL (Client URL Library) is a library and command-line tool for transferring data using various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, etc. In PHP, cURL is commonly used for making HTTP requests to other servers and fetching their responses.
🚀 Here is the Step-by-Step Guide to use cURL in PHP:
1. Enable cURL In PHP
To use cURL in PHP, ensure that the cURL extension is enabled in your PHP configuration.
You can check this by searching for 'curl' in your php.ini file. If it’s not enabled, you’ll need to enable it and restart your web server.
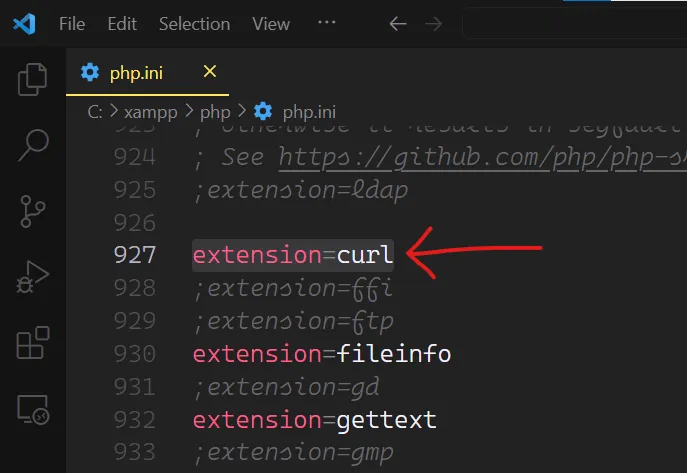
3. Making Simple GET Requests in PHP cURL
The simplest use case of cURL involves making GET requests to fetch data from a URL. Here is the basic structure of a cURL request in PHP –
curl_init()– Initialize cURL Session.curl_setopt()– Set options for a cURL transfer.curl_exec()– Execute the Request.curl_close()– close the cURL session
<?php
// Initialize a cURL session
$ch = curl_init();
// Set the URL to fetch
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/1");
// Set to return the transfer as a string instead of outputting it directly
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
// Execute the cURL session and store the response
$response = curl_exec($ch);
// Close the cURL session
curl_close($ch);
// Print the response
print_r($response);
Output:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Leanne Graham",
"username": "Bret",
"email": "[email protected]",
"address": {
"street": "Kulas Light",
"suite": "Apt. 556",
"city": "Gwenborough",
"zipcode": "92998-3874",
"geo": {
"lat": "-37.3159",
"lng": "81.1496"
}
},
"phone": "1-770-736-8031 x56442",
"website": "hildegard.org",
"company": {
"name": "Romaguera-Crona",
"catchPhrase": "Multi-layered client-server neural-net",
"bs": "harness real-time e-markets"
}
}
3. Handling POST Requests In PHP cURL
cURL also allows you to make POST requests by setting the request method to POST and providing the necessary POST data using curl_setopt(). This enables you to interact with APIs and submit data to servers.
<?php
// URL endpoint to send the POST request to
$url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts";
// Data to be sent in the POST request
$data = array(
'title' => 'foo',
'body' => 'bar',
'userId' => 5
);
// Initialize a cURL session
$ch = curl_init();
// Set the URL
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url);
// Set the request method to POST
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
// Set the request header to specify JSON content type
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, ["Content-Type: application/json"]);
// Set the POST data as JSON
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($data));
// Set to return the transfer as a string instead of outputting it directly
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
// Execute the cURL session and store the response
$response = curl_exec($ch);
// Close the cURL session
curl_close($ch);
// Print the response
print_r($response);
Output:
{
"title": "foo",
"body": "bar",
"userId": 5,
"id": 101
}
4. Customizing Requests with Options
cURL provides lots of options that allow you to customize your HTTP requests. These options include:
- setting custom request headers,
- specifying request methods,
- configuring SSL options,
- setting timeouts, and more.
Understanding these options empowers you to tailor your requests according to your specific requirements.
curl_setopt() is a function in PHP used to set options for a cURL transfer. It allows you to configure various aspects of the cURL request, such as the URL, request method, headers, data, and more.
Here’s a breakdown of how you can customize requests with options in PHP cURL:
- Initialize cURL: Start by initializing a cURL session using
curl_init(). - Set URL: Use curl_setopt() to set the URL of the request (
CURLOPT_URL). - Set Request Method: If needed, specify the request method (
GET,POST,PUT,DELETE, etc.) using curl_setopt() withCURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST. - Set Request Headers: Set request headers using curl_setopt() with
CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER. Headers are typically passed as an array. - Set Request Data: If you’re sending data with the request (e.g., form data, JSON), use curl_setopt() with
CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS. - Set Additional Options: There are many other options you can set using curl_setopt() depending on your requirements. These include timeout (
CURLOPT_TIMEOUT), follow redirects (CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION), SSL verification (CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER), and more. - Execute Request: After setting all options, execute the cURL request using curl_exec().
- Handle Response: Capture and handle the response returned by
curl_exec(). This may involve printing it, processing it, or error handling. - Close cURL Session: Close the cURL session using
curl_close()to free up resources.
Here is a demonstration:
<?php
// Initialize cURL session
$ch = curl_init();
// Set URL
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, "https://api.example.com/data");
// Set request method (optional, defaults to GET)
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST, "POST");
// Set request headers
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array(
'Content-Type: application/json',
'Authorization: Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN'
));
// Set request data (if sending data)
$data = array('key1' => 'value1', 'key2' => 'value2');
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($data));
// Set additional options (optional)
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true); // Return response as string
// Execute request
$response = curl_exec($ch);
// Check for errors
if (curl_errno($ch)) {
echo 'Curl error: ' . curl_error($ch);
}
// Close cURL session
curl_close($ch);
// Handle response
echo $response;
5. Managing Responses:
Once you’ve executed a cURL request, you’ll receive a response from the server. Depending on your settings, this response can be outputted directly, stored in a variable for further processing, or saved to a file.
Managing responses in PHP cURL involves capturing the response returned by curl_exec() and then handling it appropriately.
Here’s a general guide on how to manage responses in PHP cURL:
- Capture Response: After executing the cURL request using curl_exec(), capture the response in a variable.
- Error Handling: Check for errors using curl_errno(). If an error occurs, handle it accordingly.
- Handle Success: If the request is successful, process the response data according to your application’s logic. This may involve parsing JSON or XML data, extracting specific information, or displaying the response.
- Close cURL Session: After processing the response, close the cURL session using curl_close() to free up resources.
Here’s an example demonstrating these steps:
<?php
// Initialize cURL session
$ch = curl_init();
// Set URL
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, "https://api.example.com/data");
// Set additional options (optional)
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true); // Return response as string
// Execute request
$response = curl_exec($ch);
// Check for errors
if(curl_errno($ch)){
echo 'Curl error: ' . curl_error($ch);
// Handle error appropriately (e.g., log, display error message)
} else {
// Successful request
$http_code = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE); // Get HTTP status code
if ($http_code == 200) {
// Process response data
echo "Response received: " . $response;
// Further processing of the response (e.g., JSON decoding, data manipulation)
} else {
echo "Unexpected HTTP status code: " . $http_code;
// Handle non-200 status code appropriately (e.g., retry, error handling)
}
}
// Close cURL session
curl_close($ch);
?>
6. Handling PHP cURL Errors
Handling errors in PHP cURL involves checking for errors using curl_errno() after executing the request with curl_exec().
Here’s a guide on how to handle errors in PHP cURL:
- Check for Errors: Immediately after executing the cURL request with curl_exec(), use curl_errno() to check if any errors occurred during the request.
- Error Handling: If an error is detected, handle it appropriately. This may involve displaying an error message, logging the error, or taking corrective action.
- Close cURL Session: After handling errors (if any), close the cURL session using curl_close() to free up resources.
Here’s an example demonstrating how to handle errors in PHP cURL:
<?php
// Initialize cURL session
$ch = curl_init();
// Set URL
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, "https://api.example.com/data");
// Set additional options (optional)
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true); // Return response as string
// Execute request
$response = curl_exec($ch);
// Check for errors
if(curl_errno($ch)){
// An error occurred during the request
$error_message = curl_error($ch);
echo 'Curl error: ' . $error_message;
// Handle the error appropriately (e.g., display error message, log error)
} else {
// Successful request
$http_code = curl_getinfo($ch, CURLINFO_HTTP_CODE); // Get HTTP status code
if ($http_code == 200) {
// Process response data
echo "Response received: " . $response;
// Further processing of the response (e.g., JSON decoding, data manipulation)
} else {
echo "Unexpected HTTP status code: " . $http_code;
// Handle non-200 status code appropriately (e.g., retry, error handling)
}
}
// Close cURL session
curl_close($ch);
?>
7. Submit Files Using cURL:
To submit files using cURL in PHP, you can use the CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS option to specify a multipart/form-data request. This allows you to upload files along with other form data.
Here’s an example of how to do it:
<?php
// URL endpoint to upload the file to
$url = "https://example.com/upload.php";
// File to upload
$file_path = "/path/to/file/example.jpg";
// Initialize cURL session
$ch = curl_init();
// Set URL
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_URL, $url);
// Set request method to POST
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
// Define file fields (you can add additional form fields if needed)
$post_fields = array(
'file' => new CURLFile($file_path) // Create a CURLFile object with the file path
);
// Set POST data as multipart/form-data
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, $post_fields);
// Set additional options if needed (e.g., CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER)
// Execute request
$response = curl_exec($ch);
// Check for errors
if (curl_errno($ch)) {
echo 'Curl error: ' . curl_error($ch);
}
// Close cURL session
curl_close($ch);
// Handle response (if needed)
echo $response;
PHP cURL Advanced Techniques
Advanced techniques in PHP cURL involve leveraging various options and features to enhance functionality, security, and performance.
Here are some advanced techniques you can use with PHP cURL:
- SSL/TLS Options: Configure SSL/TLS settings for secure communication, including verifying peer and host certificates (CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYHOST), specifying certificate files (CURLOPT_CAINFO, CURLOPT_SSLCERT, CURLOPT_SSLKEY), and setting SSL version (CURLOPT_SSLVERSION).
- HTTP Authentication: Implement HTTP authentication methods such as Basic (CURLOPT_HTTPAUTH, CURLOPT_USERPWD), Digest (CURLOPT_HTTPAUTH, CURLOPT_USERPWD), and NTLM (CURLOPT_HTTPAUTH, CURLOPT_USERPWD).
- Cookies Handling: Manage cookies by enabling cookie handling (CURLOPT_COOKIEFILE, CURLOPT_COOKIEJAR), sending cookies with requests (CURLOPT_COOKIE), and customizing cookie behavior (CURLOPT_COOKIESESSION, CURLOPT_COOKIELIST).
- HTTP Headers Customization: Customize HTTP headers by setting request headers (CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER), including custom headers like User-Agent, Accept, and Referer.
- Proxy Configuration: Configure proxies for requests using options like CURLOPT_PROXY, CURLOPT_PROXYPORT, CURLOPT_PROXYTYPE, CURLOPT_PROXYUSERPWD, and CURLOPT_NOPROXY.
- Handling Redirects: Manage redirects with options such as CURLOPT_FOLLOWLOCATION, CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS, and CURLOPT_AUTOREFERER.
- Multi-Requests: Perform multiple requests concurrently using the curl_multi_functions for improved performance and efficiency.
- Streaming Responses: Handle large responses or streaming data by using options like CURLOPT_WRITEFUNCTION to process response data incrementally.
- Timeouts and Connection Limits: Set timeouts (CURLOPT_TIMEOUT, CURLOPT_CONNECTTIMEOUT) and limits (CURLOPT_MAXCONNECTS) to control request timeouts and connection limits.
- Custom Request Methods: Send custom HTTP request methods (e.g., PUT, DELETE, PATCH) using CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST.
- Handling Compression: Enable compression support using options like CURLOPT_ENCODING to automatically handle compressed responses (e.g., gzip, deflate).
- DNS Resolution Control: Control DNS resolution behavior with options such as CURLOPT_RESOLVE to specify custom DNS mappings.
References of PHP cURL:
- PHP Manual: cURL – https://www.php.net/manual/en/book.curl.php
- cURL Documentation – https://curl.se/docs/manpage.html
